The impact of state and dispositional mindfulness on prospective memory: A virtual reality study
Abstract
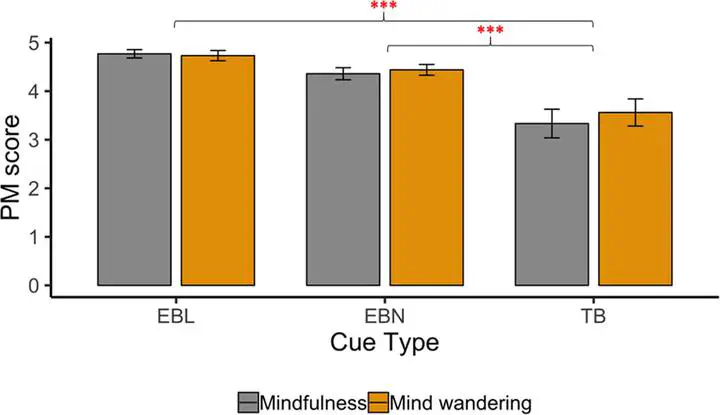
Prospective memory (PM) consists of remembering to perform an action that was previously planned. The recovery and execution of these actions require attentional resources. Mindfulness, as a state or a dispositional trait, has been associated with better attentional abilities while mind wandering is linked with attentional failures. In this study, we investigated the impact of mindfulness on PM. Eighty participants learned 15 cue-action associations. They were, then, asked to recall the actions at certain moments (time-based items) or places (event-based items) during a walk in a virtual town. Before the PM task, participants were randomly assigned to a mindfulness or mind wandering (control condition) session. Dispositional mindfulness was measured via the Five Facets Mindfulness Questionnaire (FFMQ). Although considered as two opposite states, we did not report any difference between the two groups on PM abilities. Nevertheless, the natural tendency to describe one’s own sensations (the Describing facet of the FFMQ) predicted time-based performance in both groups. We discuss different hypotheses to explain this finding in light of recent findings on the impact of mind wandering on future oriented cognition. Our main observation is a positive link between the Describing facet and time-based PM performances. We propose that this link could be due to the common association of this mindfulness facets and PM with attentional and interoceptive abilities. Additional studies are needed to explore this hypothesis.